
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become an essential component of modern corporate operations, providing firms with tools for streamlining procedures, increasing efficiency, and achieving real-time visibility across several departments. These systems combine critical company operations such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and inventory management onto a single platform, allowing for better decision-making.
However, when it comes to ERP systems, organizations must make a critical decision: whether to use an on-premise ERP system or a cloud-based ERP solution. At the same time, cloud ERP has grown in popularity because of its scalability and ease of adoption. On-premise ERP remains a strong choice for enterprises that value control, security, and customization. This book delves into the deep aspects of on-premise ERP systems, their benefits, and instances in which they are the best option.
Overview of ERP Systems
What Are ERP Systems?
ERP systems are software solutions for managing and automating fundamental company activities. By consolidating many procedures under a single interface, these systems cut redundancies, reduce errors, and deliver actionable information to promote growth.
Types of ERP Deployment Models
There are primarily two deployment models for ERP systems:
- On-Premise ERP: Installed on local servers and managed by the organization’s IT team.
- Cloud ERP: Hosted on a cloud service provider’s infrastructure and accessed via the internet.
Both deployment models aim to achieve the same goals but differ significantly in terms of cost, implementation, and flexibility. Let’s delve deeper into on-premise ERP to understand its unique benefits and use cases.
On-Premise ERP vs. Cloud ERP
Before choosing an ERP solution, it’s essential to understand the differences between on-premise and cloud ERP systems.
On-Premise ERP
On-premise ERP systems are hosted on local servers within an organization’s physical premises. They provide businesses with complete control over their software, infrastructure, and data.
Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP solutions, on the other hand, are housed on the vendor’s servers and accessible via the Internet. These systems are often subscription-based, with the vendor managing upgrades and maintenance.
Key Differences
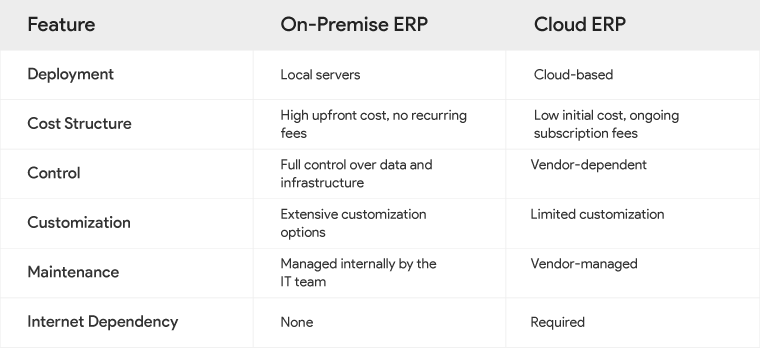
Understanding On-Premise ERP Systems
On-premise ERP systems provide a robust framework for businesses that prioritize security, control, and performance. Let’s explore their key aspects in detail.
Definition and Key Features
An on-premise ERP system is software that is deployed and managed on a company’s local infrastructure. It demands a considerable initial investment in hardware and software, but it provides unparalleled control over data and processes.
Key Features
- Data Storage: All data is stored on company-owned servers, providing enhanced privacy and security.
- Customization: Businesses can tailor the system to their specific requirements without vendor-imposed limitations.
- Integration: Seamless compatibility with legacy systems and other on-premise applications.
- Independence: No dependency on internet connectivity ensures reliable performance.
Industries That Benefit from On-Premise ERP
On-premise ERP is particularly beneficial for industries where data security, regulatory compliance, or complex customization is critical. Examples include:
1. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations handle sensitive patient data that must comply with strict privacy regulations like HIPAA. On-premise ERP ensures this data remains secure and accessible only to authorized personnel.
2. Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses often require ERP systems to integrate with shop floor machinery and other specialized tools. On-premise ERP provides the flexibility and control needed for such integrations.
3. Banking and Finance
The financial sector deals with large volumes of sensitive information. On-premise ERP systems offer the robust security measures necessary to protect this data from breaches or unauthorized access.
4. Government
Government agencies are often required to store data within national borders due to regulations on data sovereignty. On-premise ERP systems enable compliance with these requirements.
Advantages of On-Premise ERP Systems
Organizations choose on-premise ERP systems for a variety of reasons. Here are the most compelling benefits:
1. Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
On-premise ERP keeps data within the organization, reducing the risk of breaches associated with third-party cloud providers. This is particularly crucial for industries handling sensitive or classified information.
2. Greater Customization Options
Unlike cloud ERP, on-premise solutions can be extensively customized to align with specific business processes. This level of personalization ensures that the system supports unique workflows and requirements.
3. Complete Control Over Infrastructure
With on-premise ERP, businesses retain full control over their hardware, software, and data. This autonomy enables them to implement upgrades or changes without relying on external vendors.
4. Reliable Performance Without Internet Dependency
Since on-premise ERP operates independently of the internet, businesses can maintain operational continuity even during connectivity issues or outages.
5. Long-Term Cost Efficiency
While the initial cost of implementing on-premise ERP is higher, the absence of recurring subscription fees makes it a cost-effective choice in the long run for organizations planning to use the system for many years.
6. Easier Integration with Legacy Systems
Many businesses rely on legacy systems that are difficult to integrate with modern cloud-based solutions. On-premise ERP offers compatibility and flexibility for such integrations.
Scenarios Where On-Premise ERP is the Best Choice
There are specific scenarios where on-premise ERP is the preferred choice:
1. Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Industries like healthcare, finance, and government must adhere to strict data regulations. On-premise ERP ensures compliance by keeping data within organizational boundaries.
2. Businesses with Established IT Infrastructure
Organizations with robust IT teams and infrastructure can maximize the value of on-premise ERP systems while minimizing external dependency.
3. High Customization Needs
For businesses with highly specific workflows or operational requirements, the customization capabilities of on-premise ERP are unmatched.
Comparison: On-Premise ERP vs. Cloud ERP
To provide a balanced perspective, let’s compare the pros and cons of on-premise ERP and cloud ERP systems:
Pros and Cons Side-by-Side
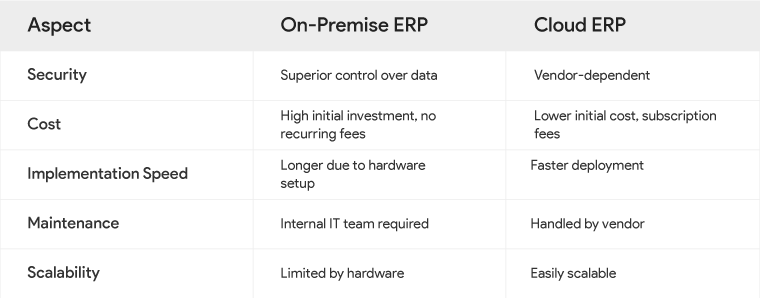
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
The decision between on-premise and cloud ERP depends on your organization’s unique needs. Here’s how you can evaluate which solution is better suited for you:
When to Choose On-Premise ERP
- Your business operates in a highly regulated industry.
- You require complete control over your data and infrastructure.
- You have an established IT team to manage maintenance.
- Long-term cost efficiency is a priority.
When to Choose Cloud ERP
- Scalability and quick implementation are key requirements.
- You lack an existing IT infrastructure.
- Your organization prefers an operational expense (OPEX) model over capital expenditure (CAPEX).
Conclusion
Summary of Benefits
On-premise ERP systems provide unparalleled control, security, and customization. They are ideal for organizations with specific regulatory or operational needs, offering reliable performance and long-term cost efficiency.
When to Choose On-Premise ERP
If your organization values data sovereignty, has a robust IT infrastructure, or requires extensive customization, on-premise ERP is the best option. While the initial investment may be significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs.
FAQs About On-Premise ERP Systems
1. What is an on-premise ERP system?
An on-premise ERP system is software installed and managed on an organization’s local servers, providing full control over data, infrastructure, and customizations.
2. How does on-premise ERP differ from cloud ERP?
On-premise ERP is hosted locally, offers greater control, and involves a higher upfront cost. Cloud ERP is hosted by a vendor, involves lower initial costs, and requires internet connectivity.
3. What are the disadvantages of on-premise ERP?
On-premise ERP requires a significant initial investment, longer implementation time, and ongoing maintenance by an internal IT team.
4. Is on-premise ERP more secure than cloud ERP?
Yes, on-premise ERP provides enhanced data security as all information is stored internally, minimizing risks associated with third-party providers.
5. Who should consider on-premise ERP?
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and government, or any organization requiring strict data control and regulatory compliance, should consider on-premise ERP.
By evaluating your organization’s priorities and understanding the unique strengths of on-premise ERP, you can make an informed decision to support your business’s growth and operational success.